Column
A control that displays its children in a vertical array.
To cause a child control to expand and fill the available vertical space set its expand property.
Examples
Column spacing
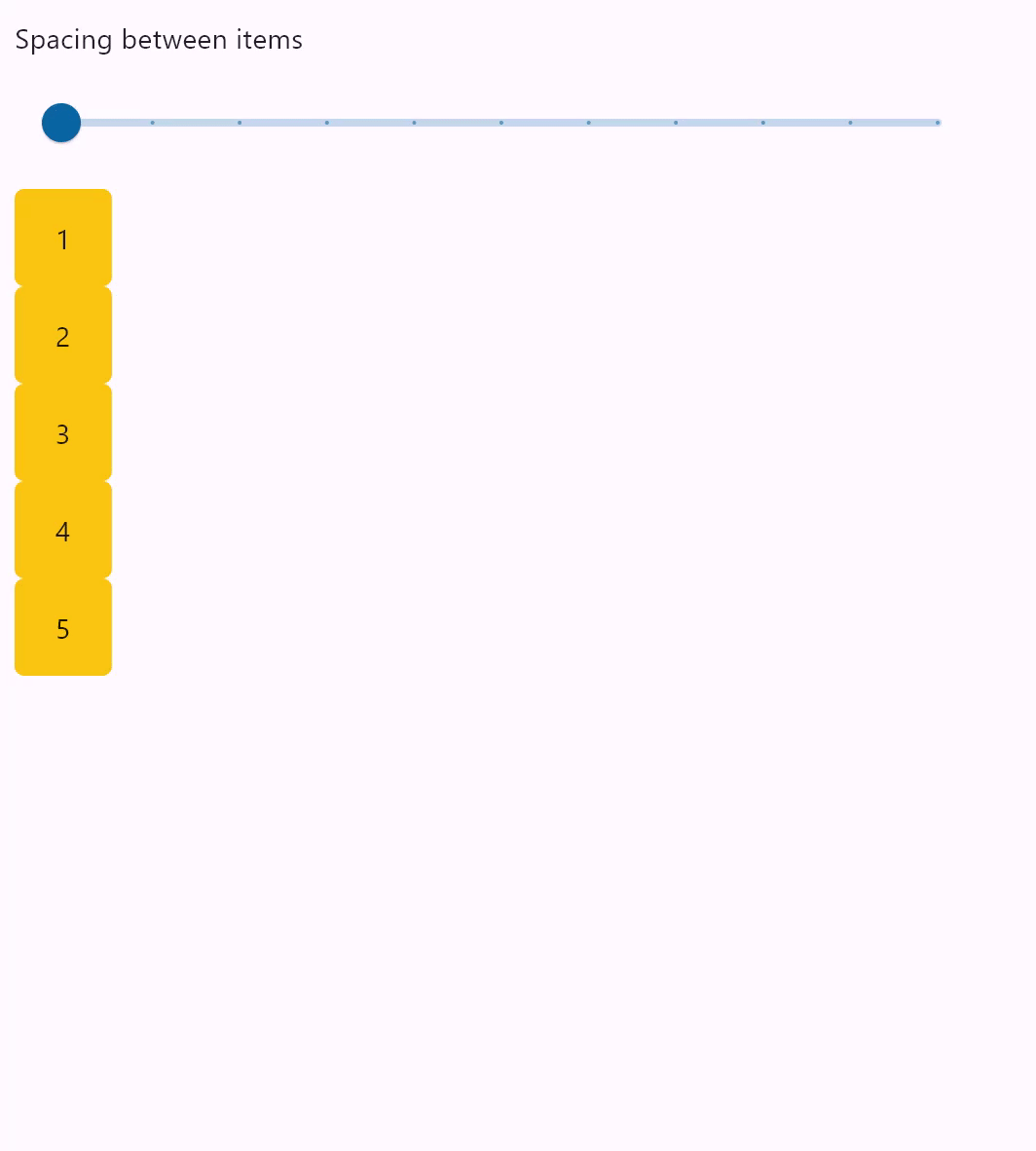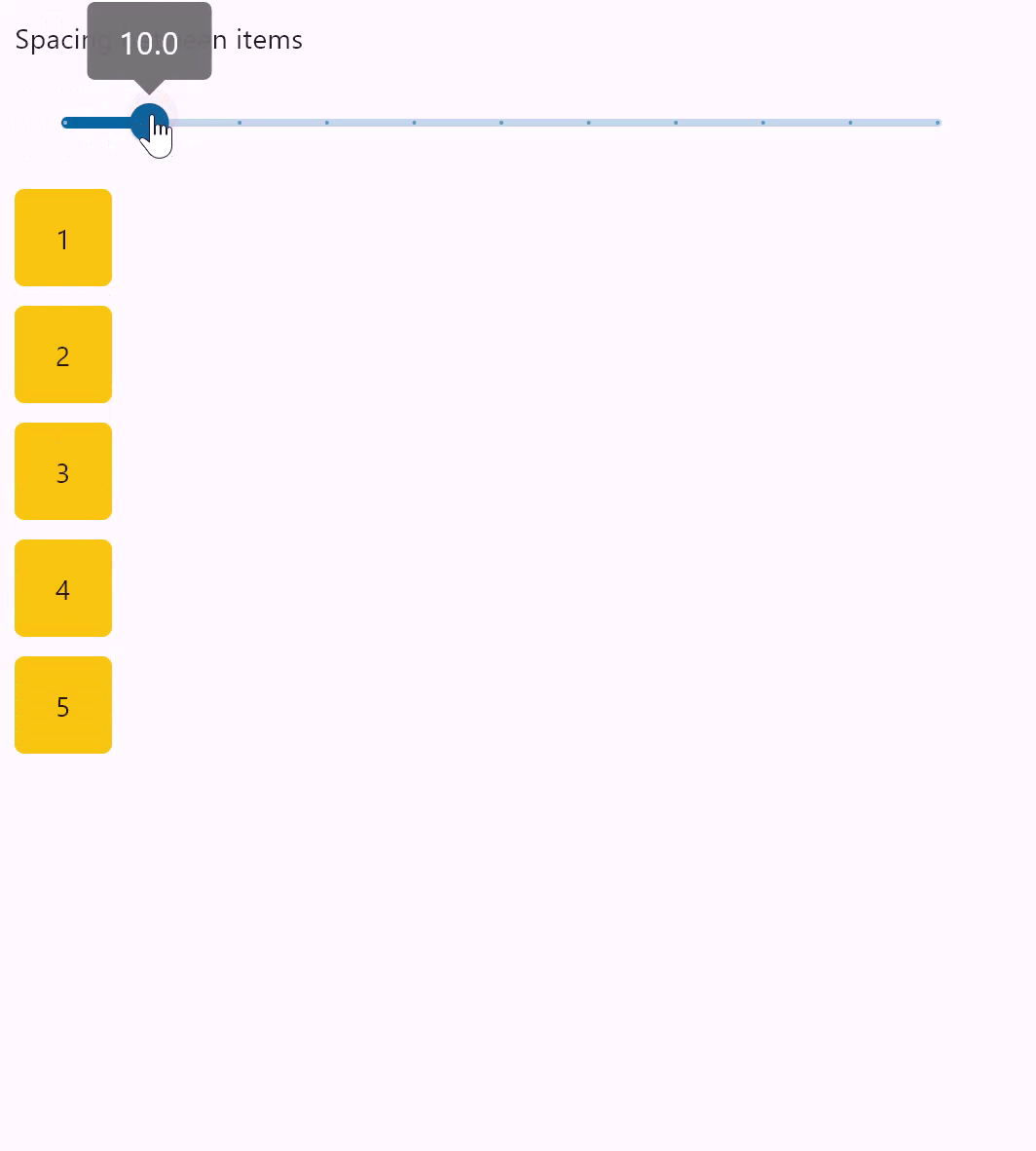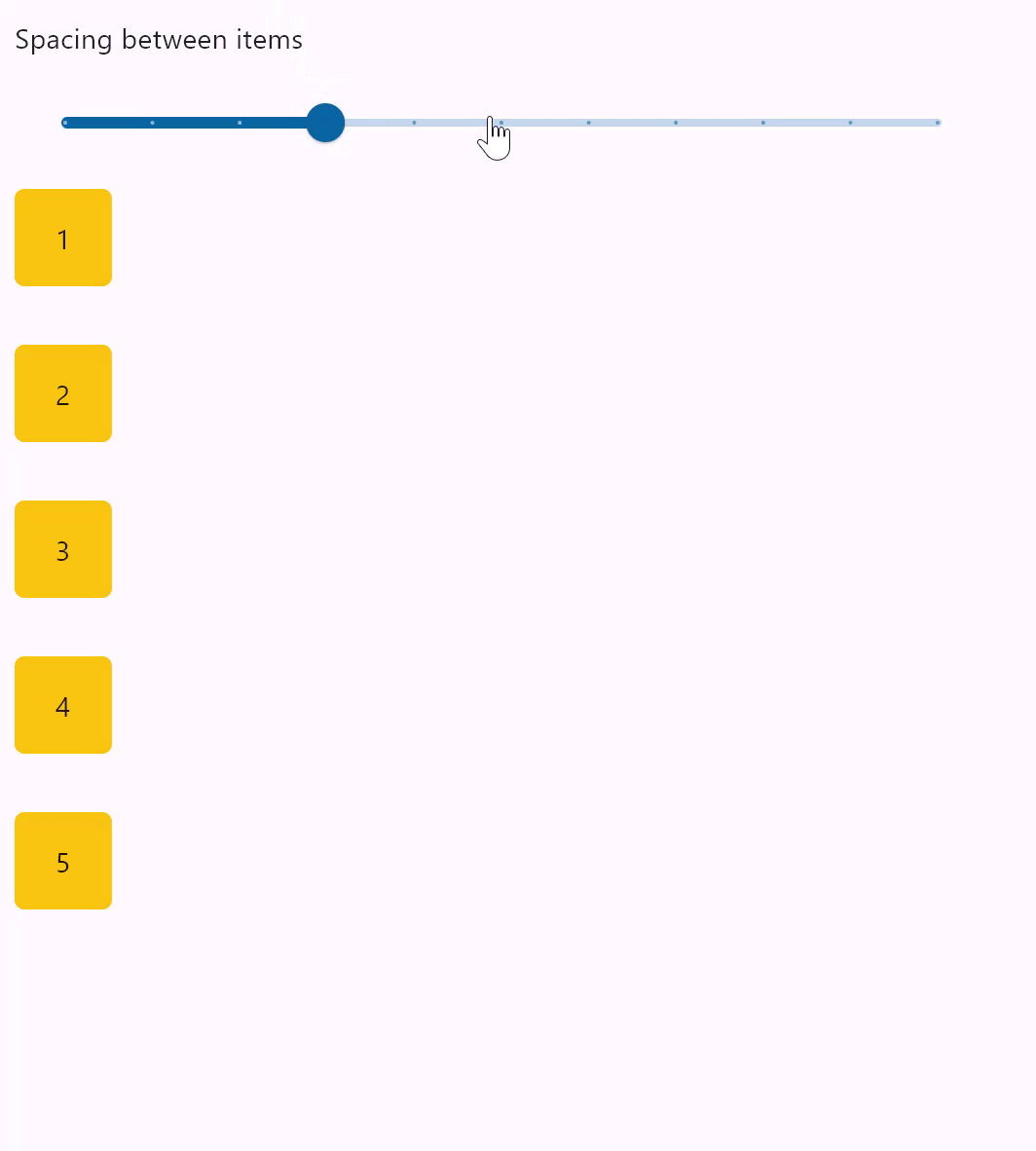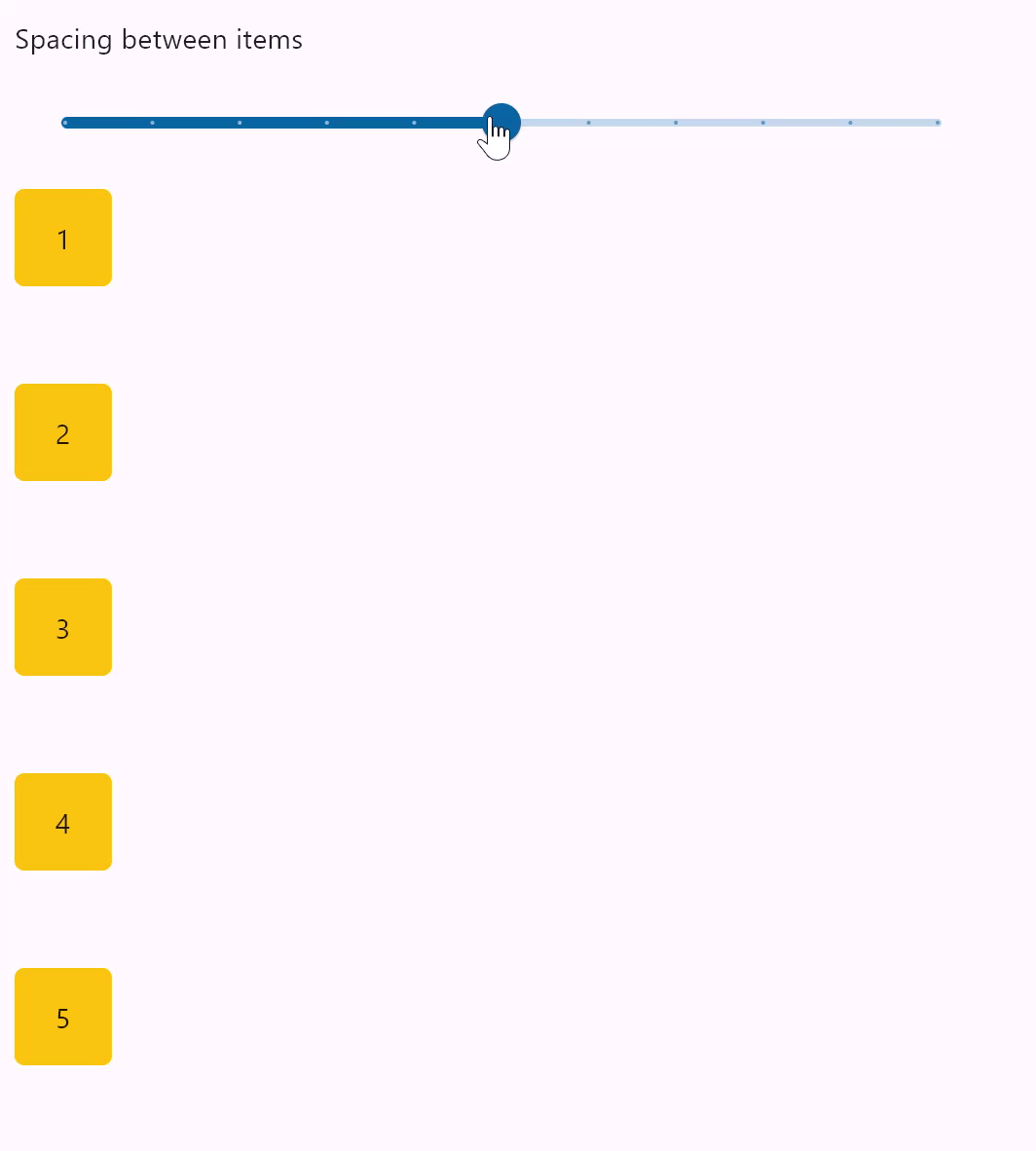
loading...
Column wrapping

loading...
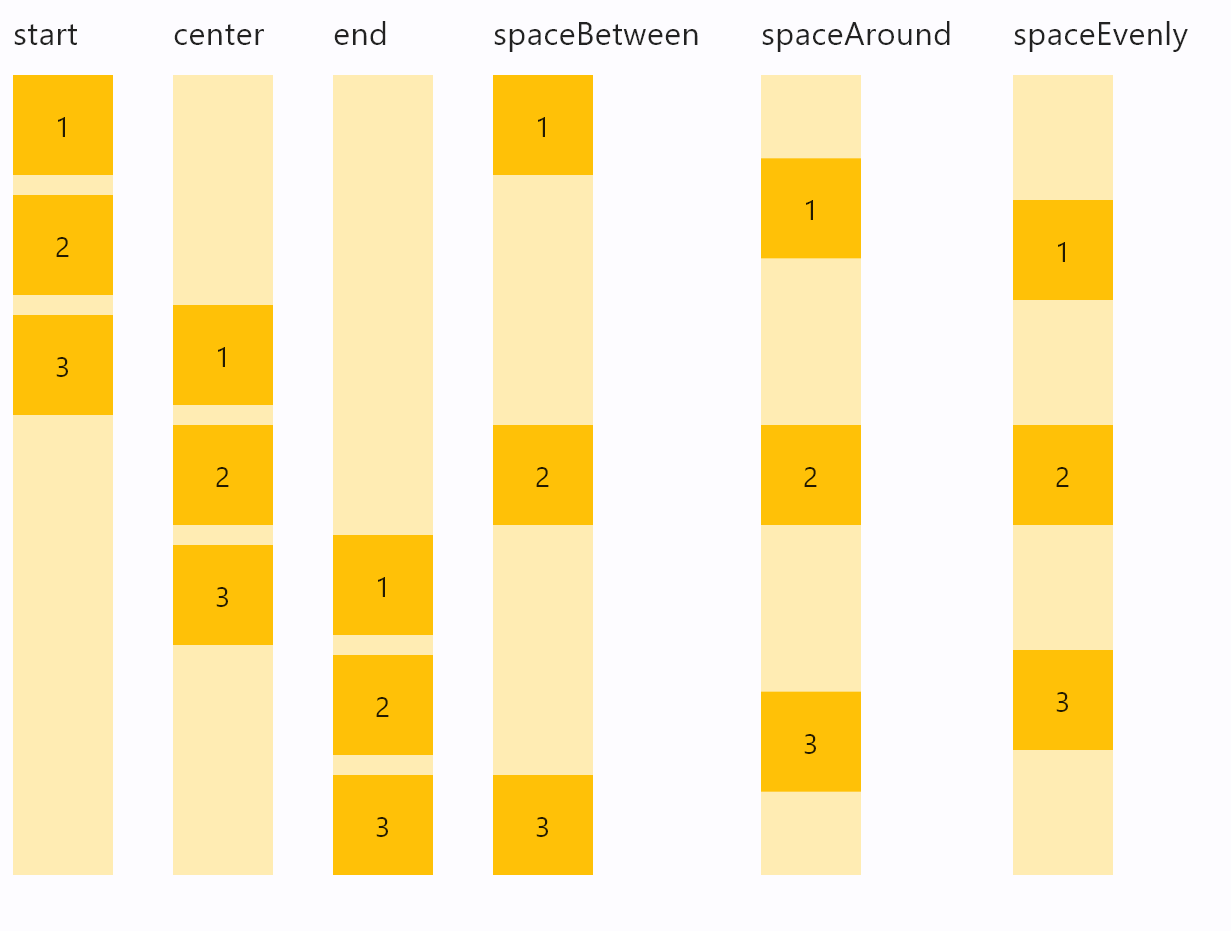
Column vertical alignments
loading...
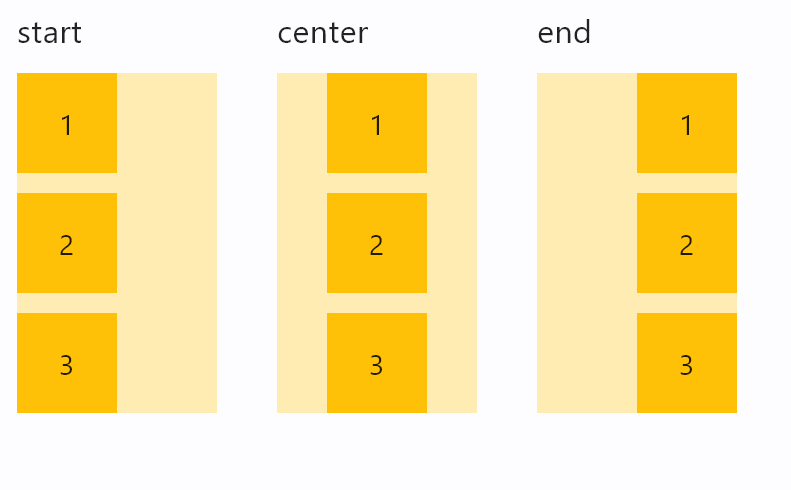
Column horizontal alignments
loading...
Infinite scroll list
The following example demonstrates adding of list items on-the-fly, as user scroll to the bottom, creating the illusion of infinite list:
loading...
Scrolling column programmatically
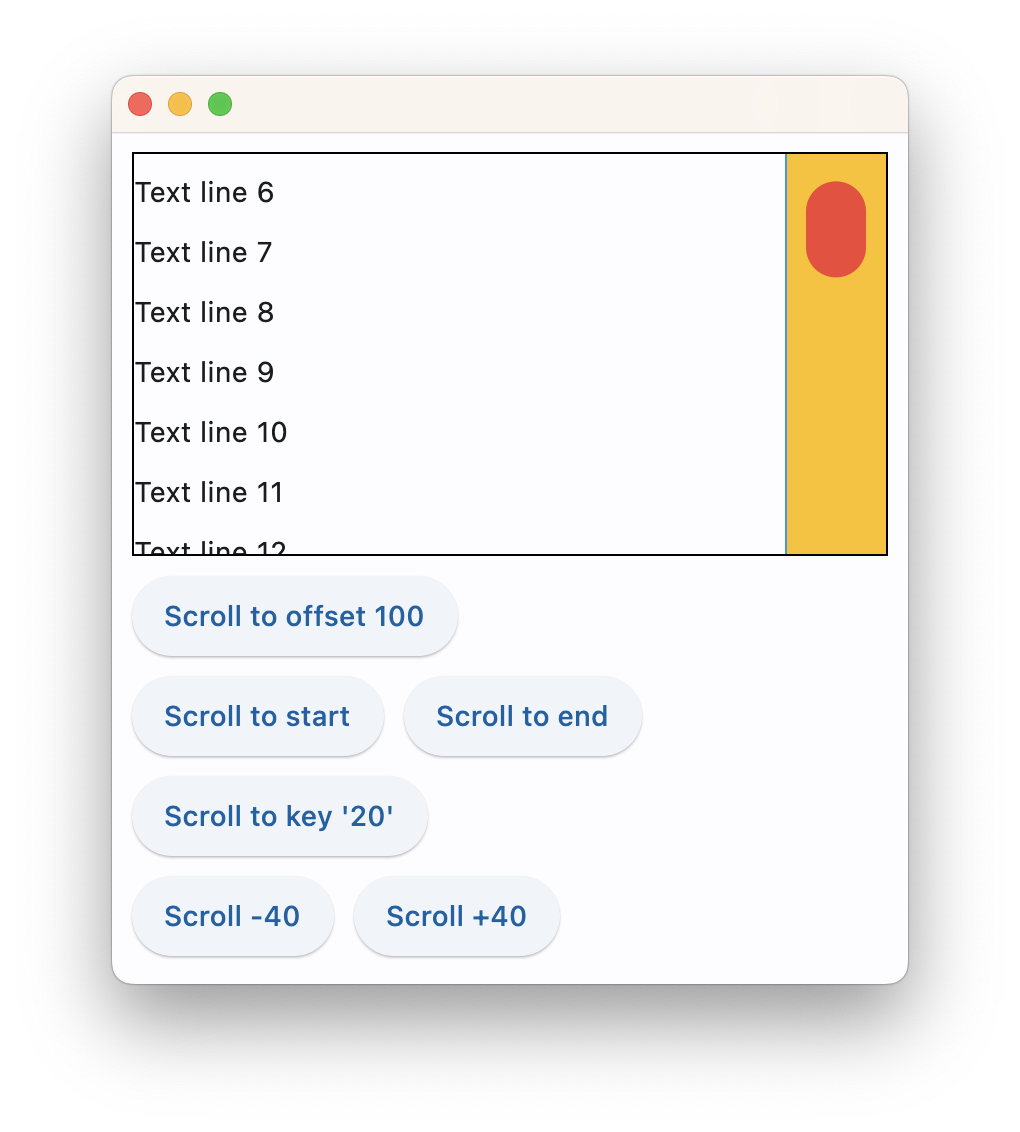
The following example demonstrates various scroll_to() options as well as defines a custom scrollbar theme:
loading...
Properties
alignment
How the child Controls should be placed vertically.
Value is of type MainAxisAlignment.
auto_scroll
True if scrollbar should automatically move its position to the end when children updated. Must be False for scroll_to() method to work.
controls
A list of Controls to display inside the Column.
horizontal_alignment
How the child Controls should be placed horizontally.
Value is of type CrossAxisAlignment and defaults
to CrossAxisAlignment.START.
on_scroll_interval
Throttling in milliseconds for on_scroll event.
Defaults to 10.
rtl
True to set text direction to right-to-left.
Defaults to False.
run_alignment
How the runs should be placed in the cross-axis when wrap=True.
Value is of type MainAxisAlignment and defaults to MainAxisAlignment.START.
run_spacing
Spacing between runs when wrap=True. Default value is 10.
scroll
Enables a vertical scrolling for the Column to prevent its content overflow.
Value is of type ScrollMode and defaults to ScrollMode.None.
spacing
Spacing between the controls.
It is applied only when alignment is set to MainAxisAlignment.START, MainAxisAlignment.END or MainAxisAlignment.CENTER.
Default value is 10 virtual pixels.
tight
Specifies how much space should be occupied vertically.
Defaults to False - allocate all space to children.
wrap
When set to True the Column will put child controls into additional columns (runs) if they don't fit a single column.
Methods
scroll_to(offset, delta, key, duration, curve)
Moves scroll position to either absolute offset, relative delta or jump to the control with specified key.
offset is an absolute value between minimum and maximum extents of a scrollable control, for example:
products.scroll_to(offset=100, duration=1000)
offset could be a negative to scroll from the end of a scrollable. For example, to scroll to the very end:
products.scroll_to(offset=-1, duration=1000)
delta allows moving scroll relatively to the current position. Use positive delta to scroll forward and negative delta to scroll backward. For example, to move scroll on 50 pixels forward:
products.scroll_to(delta=50)
key allows moving scroll position to a control with specified key. Most of Flet controls have key property which is translated to Flutter as "global key". key must be unique for the entire page/view. For example:
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
cl = ft.Column(
spacing=10,
height=200,
width=200,
scroll=ft.ScrollMode.ALWAYS,
)
for i in range(0, 50):
cl.controls.append(ft.Text(f"Text line {i}", key=str(i)))
def scroll_to_key(e):
cl.scroll_to(key="20", duration=1000)
page.add(
ft.Container(cl, border=ft.border.all(1)),
ft.ElevatedButton("Scroll to key '20'", on_click=scroll_to_key),
)
ft.app(main)
scroll_to() method won't work with ListView and GridView controls building their items dynamically.
duration is scrolling animation duration in milliseconds. Defaults to 0 - no animation.
curve configures animation curve. Property value is AnimationCurve enum.
Defaults to AnimationCurve.EASE.
Events
on_scroll
Fires when scroll position is changed by a user.
Event handler argument is an instance of OnScrollEvent class.
Expanding children
When a child Control is placed into a Column you can "expand" it to fill the available space. Every Control has expand property that can have either a boolean value (True - expand control to fill all available space) or an integer - an "expand factor" specifying how to divide a free space with other expanded child controls. For example, this code creates a column with a Container taking all available space and a Text control at the bottom serving as a status bar:
r = ft.Column([
ft.Container(expand=True, content=ft.Text("Here is search results")),
ft.Text("Records found: 10")
])
The following example with numeric expand factors creates a Column with 3 containers in it and having heights of 20% (1/5), 60% (3/5) and 20% (1/5) respectively:
r = ft.Column([
ft.Container(expand=1, content=ft.Text("Header")),
ft.Container(expand=3, content=ft.Text("Body")),
ft.Container(expand=1, content=ft.Text("Footer"))
])
In general, the resulting height of a child in percents is calculated as expand / sum(all expands) * 100%.
If you need to give the child Control of the Column the flexibility to expand to fill the available space vertically but not require it to fill the available space, set its expand_loose property to True.